Background Information
A Network Topology is a visual representation of how pieces of hardware, nodes, or connections are arranged in relation to one another. Often this Topology can give critical insight into how devices are connected and can give some general insight into how the overall network is performing.
Knowing how to make a Network Topology is often the key to building a secure, resilient, and easy-to-maintain network.
What are Nodes?
Nodes, or Network Nodes, are the connection points among network devices. This can include devices such as routers, printers, switches, servers, and any other device that can send and receive data from one endpoint to the other. Often times the definition of a node can depend on the network and the protocol layer.
Different Types of Network Topology Layouts
While there is no one-size-fits-all option when it comes to creating a Network Topology, there are different types of configurations that are suitable for different purposes depending on the size of your network and the objectives you are trying to fulfill.
Point to Point
Point to Point is the simplest network Topology that connects one node directly with another. Often times this type of Topology is used to connect two independent systems together. The connection can be anything from a physical connection through a Wide Area Network (WAN) or a connection made through a satellite line.

| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| The connection is private. Data that is shared from one device is only shared with the device that is connected to the other point. Often times this type of Topology is the most cost straightforward and cost-effective. | If the connection is ever broken, then the whole network will stop working. Any device that is on this type of topology will suffer if the connection is broken. |
Bus
A Bus Topology is a network setup that sees multiple nodes connected through a single cable which is referred to as a Bus. Any signal that is generated from a source node travels through the Bus cable and to all workstations that are connected to the one Bus cable to find the intended recipient with a specific IP address.

| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| It's a simple network for linear connection of nodes, and it is very efficient for small networks. The cable length requirement is not as demanding as other networks and allows for a good deal of modularity when adding or removing devices without significant impact on other devices. | Not good for large networks, especially when troubleshooting an issue with network failure. In addition, bandwidth is shared between devices, so the more devices that are added to this type of Topology will impact network performance. If the main Bus cable fails then the whole network can experience connection loss, or part of the network can experience a loss in connection. |
Single-Ring
Single-Ring Topology is where all the nodes are arranged in a ring, where each device node has two neighbors. This kind of network is half-duplexed, meaning that the data travels in one direction through each node to reach its destination IP.
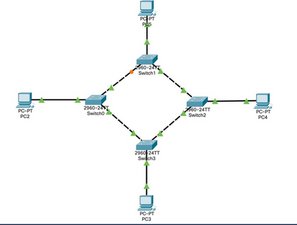
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| If this kind of Topology is used in a large network then repeaters can be used to ensure that packets arrive correctly without data loss. In addition, Single-Ring Topologies can be reliable, inexpensive, and easy to troubleshoot issues with misconfigurations on the network. | Single-Ring Topologies can be vulnerable if they are not properly managed. Since the flow of data moves between nodes along the ring, then if one node goes down then the whole network can be taken with it. There is also the issue of scalability as each device shares bandwidth, so more devices can potentially add to communication delays, along with the issue that the network must be taken offline to reconfigure, add, or remove nodes. |
Dual-Ring
Dual-Ring Topologies still feature the same node arrangement of Single-Ring Topologies, where each device has two neighboring nodes, but the key feature is that each node has a second connection between each node. This type of Topology has full duplexing, which allows data to move in both directions.

| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Data can be sent in both clockwise and counterclockwise directions along the network. The second layer also provides a layer of redundancy, and security, should the first layer fail for any reason. | While Dual-Ring can solve some of the core issues that exist in the Single-Ring Topology, they still share many of the same issues. Primarily with the issue of lack of scalability when adding devices, and communication delays if a node fails. |
Star
One of the most common Topologies, Star Topologies are arranged so that all nodes are connected to a network hub. This hub acts as means of managing data transmission as any information that is sent from any node that is on the network will pass through the central hub to reach its destination.
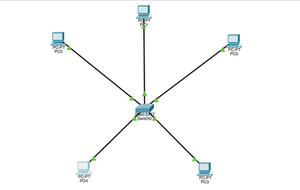
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Star Topologies are extremely convenient as they allow you to manage your network from one single point. This type of Topology also allows for devices to be added or removed, without having any kind of network downtime. In addition, this kind of layout uses relatively little cabling to fully connect your network nodes and makes troubleshooting issues on your network extremely easy. | If something were to cause the central hub to go down, then the rest of the network won't be able to function. There is also the issue with the overall bandwidth and performance being limited to the central hub itself. |
Tree
Tree Topologies get their name from how the central hub acts as a base, or trunk, of the network. the network nodes would extend outwards in a branch-like way. Unlike the Star Topology, a Tree Topology has a parent-child hierarchy with how the nodes are arranged.

| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| The Tree Topology borrows elements of both the Star and Bus Topologies, especially the aspects of scalability, straightforward error troubleshooting, and modularity of the branches | Much like Star Topology, the whole network depends on the health of the central hub. Tree Topologies can also be more difficult to manage as more nodes are added, and can quickly become more costly due to the amount of cabling needed to connect each device. |
Mesh
Mesh Topologies are interconnected structures where nodes have multiple connections to one another. Mesh Topologies can either be Partial-Mesh Topologies, where a few nodes have two or three connections, or Full-Mesh Topologies where all the nodes are fully interconnected.

| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Mesh topologies are often very reliable and stable due to the complex degree of interconnectivity between the nodes. This makes the network reliable and keeps the network from going offline due to a single device. | Mesh Topologies are often very costly and time-consuming due to the amount of cable that is required between nodes. |
Hybrid
Hybrid Topologies combine multiple topology structures into one network structure. An example of this is the Tree Topology as it combines both the Bus and Star Topologies. Often times Hybrid Topologies are found in networks that need to support a large number of users and need to meet organization-specific requirements.

| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| The biggest advantage of a Hybrid Topology is that it has a great deal of flexibility as it has very few limitations of the structure itself | As Hybrid Topologies become more complex, they can become significantly more difficult to troubleshoot, and costly depending on the number of connections needed and the experience needed from the administrator to keep things functioning optimally. |



0 comentários